IoT in manufacturing is the difference between reacting to problems after they happen and solving them before they do. But if you are still trying to cut through all the noise and figure out what is actually working on the ground, you are not alone.
Should you invest in predictive maintenance? Should you rethink your entire factory architecture around digital twins? Or start small and scale from there? The decisions are big. The risks are real. And the tech stack is evolving fast.
So, in this article, we will break it all down. From the fundamentals of IoT in manufacturing to the challenges, the real-world use cases, and how smart factories are already running at scale.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to everyday objects—such as sensors, machines, and appliances—connected to the internet, allowing them to collect and share data autonomously.
This creates an interconnected network of devices that can monitor, measure, and respond instantly without human input.
What is IoT in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the Industrial Internet of Things is known as Industrial IoT (IIoT). It brings sensors, machines, and control systems online to generate real-time insights.
These insights have a direct impact on production, quality, safety, and sustainability. IIoT is already huge. The global IIoT market reached $194 billion in 2024, rising to over $286 billion by 2029, at an 8.1% CAGR. However, when considering the broader IoT in manufacturing, including software and services, the market becomes even larger.
But what is driving this boom?
IIoT ties together machines and humans into an intelligent fabric. It brings real-time data, machine health, and performance tracking. It replaces guesswork with actionable insights. And it is scaled across industries—from automotive to pharmaceuticals, food production to energy.
The Impact of IoT in Manufacturing
Implementing IoT, or more precisely Industrial IoT (IIoT), in manufacturing transforms operations by offering unprecedented visibility and control. IIoT systems collect detailed, real-time data from machines, the environment, and the supply chain.
This depth of insight drives smarter decisions across design, production, and management. So, it is no longer guesswork; it is data-driven precision, fueling innovation and agility.
In real-world settings, organizations that invested in Operational Security experience up to 70% fewer machine breakdowns, thanks to intelligent maintenance. That cuts downtime and extends asset lifespan, boosting profitability.
Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
The majority sees IoT as a tech upgrade. But it is more than that. It is a transformation layer across the entire manufacturing value chain. When implemented effectively, it unlocks faster decision-making, higher productivity, lower waste, and more effective roles for the workforce.
Here is how:
Flexibility to Meet Changing Demand
Markets shift fast. Demand can spike overnight. Raw materials might get delayed.
With IoT, real-time data gives instant visibility into machine capacity, labor availability, and inventory positions. That means you can pivot quickly—adjust batch sizes, reroute production, or reassign shifts—without waiting for end-of-day reports.
Sustainability-Focused Approach
Every manufacturer is under pressure to reduce environmental impact. But you can not manage what you do not measure.
IoT sensors make energy usage, emissions, and waste streams visible in real time. That enables better control. Instead of running sustainability as a siloed initiative, it becomes embedded in operations — measurable, auditable, and continuously optimized.
Better Roles for the Workforce
There is a myth that IoT replaces people. In reality, it redefines their roles for the better. When machines can self-report and alert based on conditions, operators spend less time checking gauges and more time solving problems.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing IoT in Manufacturing?
While the benefits of IoT are significant, getting there is not always easy. Deploying connected systems in manufacturing presents several significant challenges.
Avoiding Data Overload
The first challenge is one of scale. Once a factory is fully wired with sensors, the volume of data being generated can be overwhelming. Machines report on temperature, vibration, location, pressure, output quality—and that is just the start.
Without the right filters, dashboards, or alerting systems, teams can become overwhelmed by data. Not every data point is valuable at the moment.
Ensuring System Reliability
Manufacturing environments are tough. Heat, dust, moisture, and vibration can destroy poorly designed electronics.
An IoT solution is a physical presence inside the factory. And if it goes offline unexpectedly, it can stall production, skew data, or cause operators to make poor decisions.
System reliability needs to be engineered from the ground up. That means ruggedized devices, edge computing for offline operation, and built-in redundancy across the network.
Real-Time Data Collection and Analysis
This is the beating heart of IoT in manufacturing. Every advantage—from predictive maintenance to process optimization—starts with real-time data.
Real-time monitoring transforms visibility. Instead of waiting for a report at the end of a shift, managers and engineers can see exactly what is happening right now. Which machines are running hot? Which batches are showing deviation? Where is the inventory backing up?
But more importantly, this data feeds live dashboards, control systems, and alerts. Once you have live data flowing, every day becomes an opportunity to optimize.
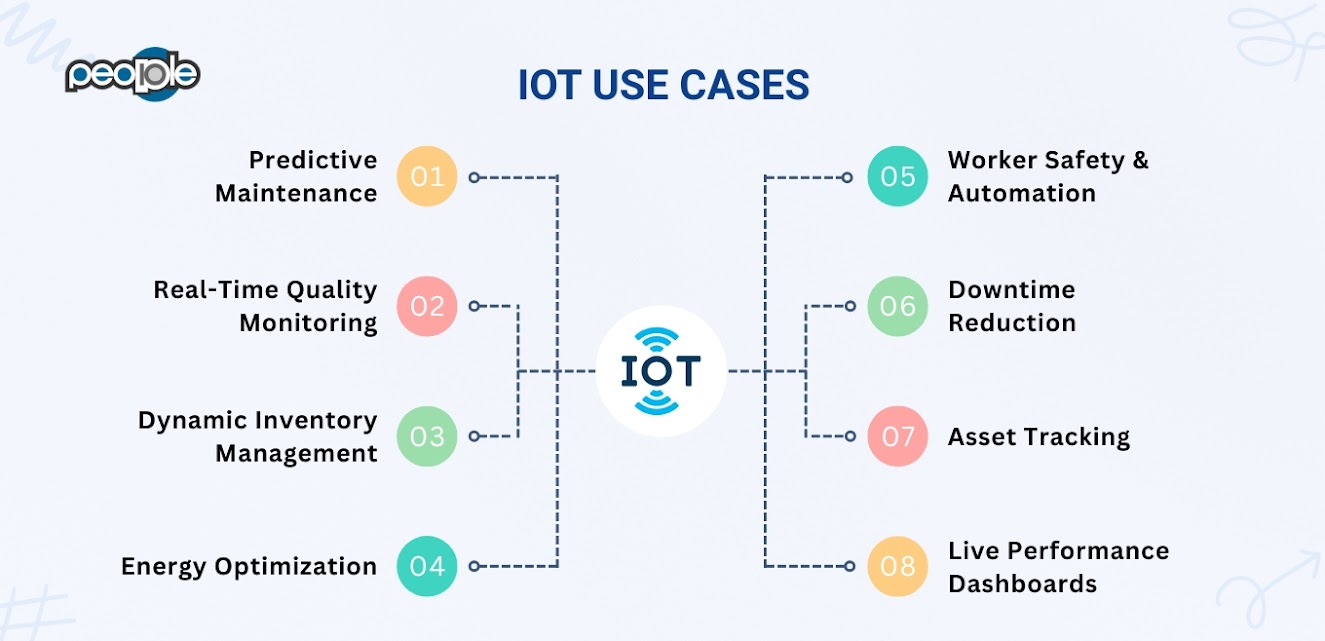
Use Cases of IoT in Manufacturing
Now, let us bring it all together with real-world scenarios that demonstrate how IoT is transforming the way factories operate.
- Predictive Maintenance: Instead of waiting for equipment to fail, smart sensors monitor key indicators like heat, vibration, and pressure. When those values drift from normal, the system can schedule service before a breakdown occurs. This reduces downtime and protects critical assets.
- Worker Safety and Automation: Wearable sensors monitor worker locations and vital signs. If someone enters a dangerous area or shows signs of fatigue, the system can intervene. Robots and cobots adjust their movements based on real-time worker positioning, ensuring a safer collaborative environment.
Each of these use cases demonstrates how the Internet of Things enables manufacturing to be smarter, safer, and more responsive.
IoT Solutions for Manufacturing
To navigate these challenges and unlock the full potential of IoT, manufacturers are adopting purpose-built solutions.
Some are cloud-native platforms that integrate with existing ERP, MES, and SCADA systems. Others are hardware suites—complete with edge devices, gateways, and protocol converters. And some offer end-to-end services, from installation to analytics.
The key is choosing solutions that are:
- Modular and scalable
- Interoperable with legacy systems
- Secure, with end-to-end encryption
- Designed for industrial environments
- Supported by strong analytics and visualization tools
No two factories are the same. The best solutions are flexible enough to adapt to your setup, while standard enough to avoid vendor lock-in.
How Does IoT Enable Smart Manufacturing?
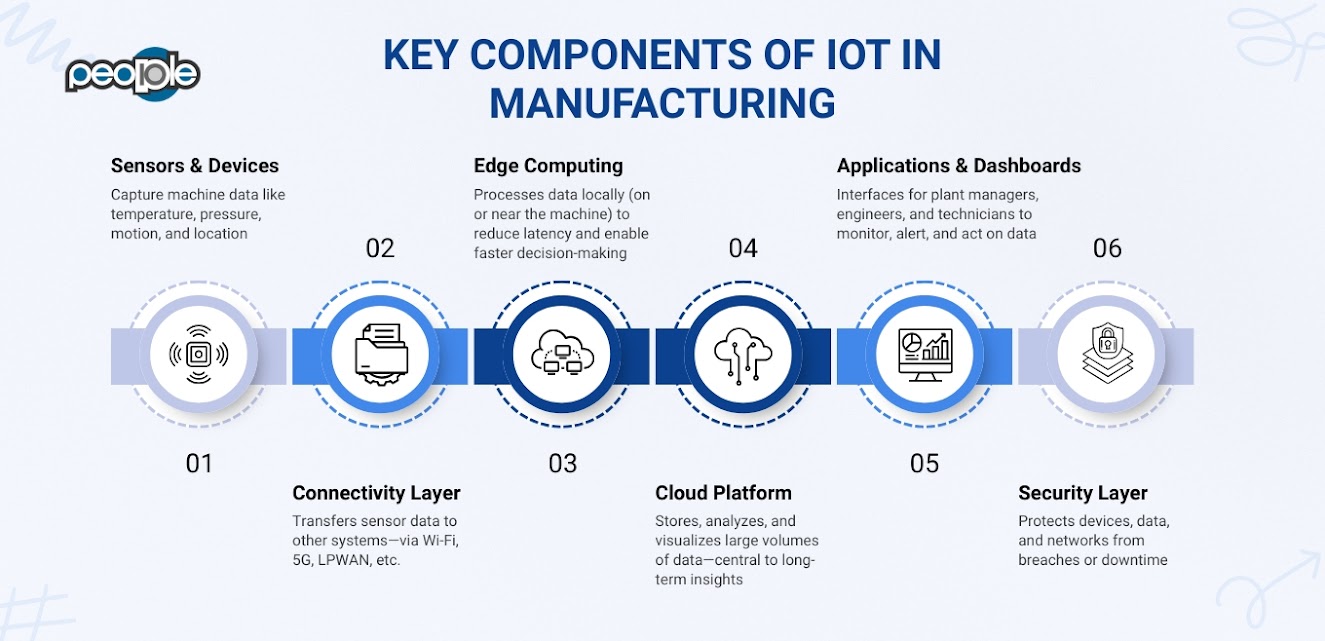
Smart manufacturing is a shift in how factories operate—from being reactive and isolated to being proactive, connected, and self-optimizing.
At the center of this shift is IoT.
From Machines to Intelligence
Traditionally, machines operated in silos. They performed their tasks independently, and if something went wrong, someone had to notice, investigate, and act.
With IoT, those machines become data sources. They share information about what is happening right now. This data can include temperature, speed, torque, energy use, cycle time, error rates, and much more.
But it is not just about collecting that data. What makes manufacturing smart is what happens next: the system analyzes, interprets, and acts on it, all in real-time.
Connecting Systems Across the Shop Floor
IoT acts as the connective tissue between everything: machines, people, products, and systems.
A smart production line might involve:
- Sensors track part dimensions and quality in real time
- Robots adjusting behavior based on worker proximity
- Machines communicating with each other to balance load
- Inventory systems triggering orders when stock drops
- Maintenance systems flagging machines before they fail
This interconnectedness is what makes the factory “smart.” Information is not trapped inside machines, but it flows across the entire ecosystem, enabling coordinated decisions.
Closing the Loop with Intelligence
Perhaps the most powerful part of IoT in manufacturing is the feedback loop it creates.
Data comes in. It is analyzed. Insights are generated. But then the system uses those insights to improve itself.
For example:
- A quality inspection sensor identifies a recurring defect
- That insight is shared with the machine control system
- The machine fine-tunes its process parameters in real time
- The defect rate drops — without any manual intervention
This kind of closed-loop control is transformative, which means the factory can continuously learn and evolve, driven by real-time feedback from every part of the system.
Applications of IoT in Smart Manufacturing
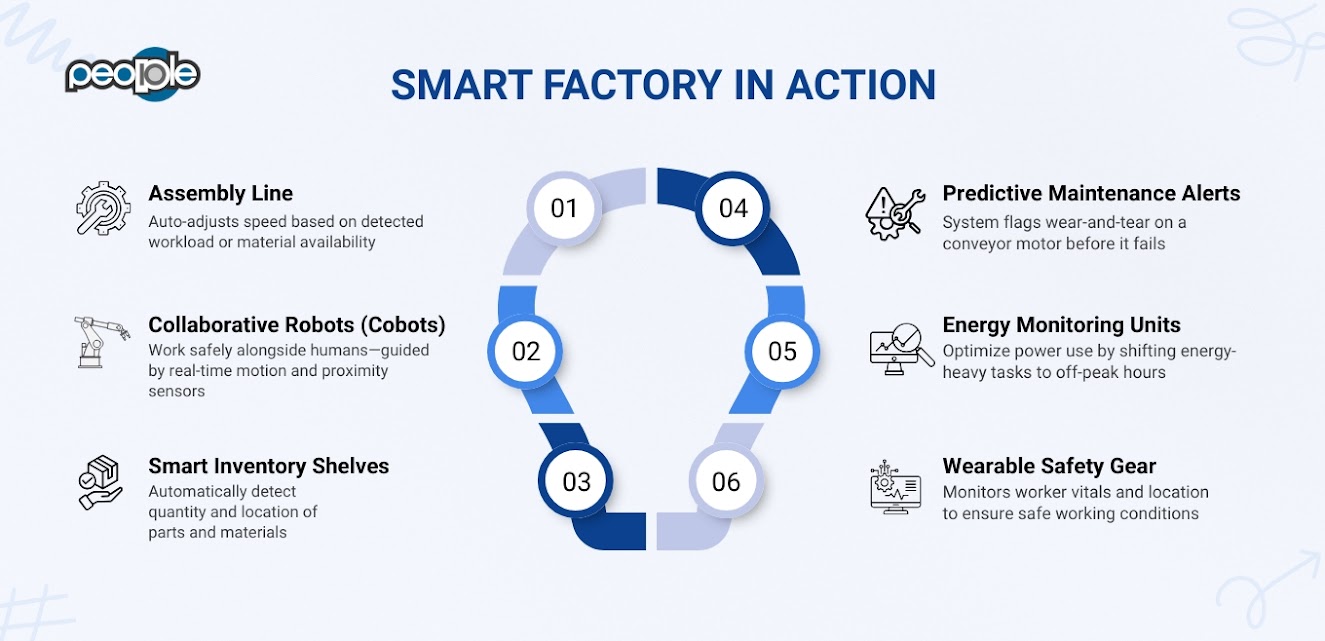
IoT is showing up in real, tangible ways in factories around the world. Below are some of the most common and impactful applications, along with examples that illustrate how they are actually implemented in practice.
Automation and Efficiency: Driving Smart Manufacturing with IoT
IoT enables automation by allowing machines and systems to operate autonomously, reducing the need for human intervention.
Sensors and connected devices continuously monitor and adjust production processes in real-time, optimizing workflows, reducing errors, and ensuring operational efficiency at all stages of manufacturing.
Predictive Maintenance: Catching Issues Before They Become Problems
Maintenance used to be a guessing game. Either you fixed things on a schedule (even if they did not need fixing), or you waited until something broke and scrambled to get it back online.
IoT changes that completely.
With sensors installed on machines, you can monitor critical indicators like vibration, heat, humidity, and power draw. These readings tell you how the equipment is behaving in real time.
When patterns shift—say, a motor starts vibrating more than usual—that is an early warning sign. Instead of waiting for a breakdown, your system can flag the issue, create a work order, or even initiate a shutdown sequence to prevent damage.
This keeps machines running longer, reduces unplanned downtime, and saves money on emergency repairs. It also helps optimize your parts inventory — since you only replace what actually needs attention.
Energy Consumption Monitoring: Saving Costs, Reducing Waste
Factories use a lot of energy. But without detailed visibility, you may not know where the waste is happening — or when you are using more than you should.
IoT-enabled meters can track electricity, gas, water, and compressed air usage across every machine, line, or building.
This helps you pinpoint inefficiencies. Maybe a machine draws too much power in idle mode. Maybe the lighting is left on in unused zones. Maybe a piece of equipment is over-consuming during startup.
Once you know where the energy is going, you can reduce it — automatically. Smart controls can shut down idle machines, optimize HVAC systems, or even shift power-intensive tasks to off-peak hours. Hence, it directly cuts operational costs.
Worker Safety and Operational Efficiency: Protecting People, Perfecting Processes
Along with connecting machines, IoT protects people, too.
Wearables like smart helmets, vests, or wristbands can monitor worker location, movement, and even vital signs. If someone enters a restricted zone or shows signs of fatigue, the system can alert supervisors immediately.
Similarly, proximity sensors on forklifts or robotic arms can slow or stop equipment if a human gets too close — preventing accidents before they happen.
Generating Value from IoT Data: Turning Data into Decisions
At the end of the day, IoT is really about insight. It is about understanding what is happening and acting on it.
The data collected from machines, processes, and people feeds into dashboards, alerts, and analytics engines.
What is your true equipment effectiveness? Which lines are bottlenecks? What shift delivers the best performance? Where is your waste coming from?
By visualizing this information clearly, plant managers and engineers can make smarter, faster decisions every single day.
Build the Smart Factory You Envision—With a Team That Gets It Done
At People10, we help manufacturers harness the power of connected systems—transforming data into real-time decisions, and operations into intelligent ecosystems.
Whether you are optimizing one line or rethinking your entire factory architecture, our teams bring the engineering muscle and IoT expertise to accelerate your journey.
We work across industries—from automotive to consumer goods, discrete to process manufacturing—delivering solutions that are scalable, secure, and built for real-world conditions.
Ready to Turn Your Factory into a Smart Factory?
Let us talk about how a high-performing product team can bring your IoT vision to life—on time, and built to last.
Author
Nandakumar excels in delivering diverse solutions from mobile apps to complex enterprise systems. At People10, he continues to drive success with a focus on customer satisfaction and innovative technology solutions.



